It’s believed about 10 million Americans are deficient in iron. So, if you’ve been feeling extra fatigued lately, there’s a chance low-iron may be to blame. While the body is able to store about 1 to 3 years worth of iron, it’s really easy for your stores to run low. Why? Not only is iron a notoriously hard mineral to absorb, it can also be easily lost. And while vegetarian and vegan diets are often linked with iron deficiency, steak eaters are equally at risk to go low on this essential mineral that plays a variety of important roles in the body.
Keep reading to see what are common symptoms of low iron and what you can do to get your energy back up.
Who is at Risk for Iron Deficiency?
Even if you think you’re eating enough iron-rich foods, much of what we drink or eat can also suppress iron absorption. Love coffee or tea? The tannins found in coffee, tea, and wine can block iron absorption. High amounts of calcium in dairy, as well as proteins in soy, phytates found in unsoaked grains, and beans can block iron absorption too. (1)
Once food hits our gut, it’s our stomach acid that creates the right conditions for optimal iron absorbability. If you have low stomach acid or take drugs for acid reflux that work to reduce stomach acid, both can block the body from absorbing iron and possibly lead to deficiency. Gut issues like IBS and leaky gut can also make iron difficult to absorb.
While we also naturally lose a small amount of iron daily from shedding cells and sweating, iron loss can be more severe when caused by blood loss from things like internal ulcers, injury, or monthly menstruation (especially if heavy).
You may also have low iron if you (2):
- Are a vegetarian or vegan (3, 4)
- Are a pregnant, breastfeeding, or menstruating woman
- Have digestive issues, like IBS or leaky gut, which can affect absorption
- Have had blood loss due to ulcers, accident, or surgery
- Take drugs that reduce stomach acid (prilosec, omeprazole, etc)
- Are over the age of 65
- Have parasites or have had an infection
- Are an athlete (5)
Health Fact: 20% of women, 50% of pregnant women, and 3% of men are iron deficient. (6)
 What are the Benefits of Iron For Health?
What are the Benefits of Iron For Health?
Iron (Fe) is an essential mineral that we must get through our diets. Iron is important to keep us healthy.
Iron Is Needed to Keep Our Cells Oxygenated
Our red blood cells contain an important protein called hemoglobin which helps them carry fresh oxygen throughout the body. About 70% of all the iron in our body can be found in our red blood cells. Hemoglobin, which gives blood its color, can only carry oxygen to our cells effectively if it’s bound to iron. Once we start to get low on iron, our red blood cells can have a hard time keeping up with our body’s oxygen demand.
Iron Helps Turn Food Into Energy
Enzymes are types of proteins that catalyze or increase the rate of chemical reactions in our cells. Many require iron, including those that convert the nutrients from our food into an important form of cell energy called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). (7)
Iron Is Important For Immunity
If you get sick frequently, low iron may be to blame. Necessary for strong immune cells and a strong immune response, iron is key if you want your body to be able to fight off infections and keep the sniffles away. (8)
Iron Helps with Mood, Concentration, Memory and Focus
Besides helping with oxygenating the brain, iron is also important in the production of myelin. This protective layer, also referred to as a “sheath”, forms around nerve cells and allows electrical signals to travel efficiently from cell to cell. When iron is low, our nerve function becomes impaired. This can cause brain fog to set in and we can find it hard to concentrate. (9)
Iron is also important in the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, the happy hormone, and dopamine which helps with productivity and focus. Getting your iron levels back on track can help keep your brain firing on all cylinders so you can live your best life. (10)
Iron Is Important For a Healthy Pregnancy
About 50% of women who become pregnant suffer from iron deficiency. While the average daily recommended iron for an adult woman is about 18 mg per day, a pregnant woman’s body demands upwards of 27 mg of iron each day. Iron is required for the development of a healthy baby and getting enough iron during pregnancy is vital. If iron deficiency (anemia) becomes more serious it can lead to premature birth, having a low birth weight baby and even postpartum depression. In severe situations it can lead to miscarriage. (11)

What are Symptoms of Low Iron?
If you’re low in iron it’s hard for your blood to stay oxygenated which is why you may feel weak, exhausted, or short of breath when your stores are low. When our iron levels drop so low that it affects our hemoglobin, this is what is called anemia.
Symptoms of low iron can sometimes remain hidden unless you become anemic. But not always.
Symptoms of low iron and iron deficiency can include:
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Feelings of weakness
- Fatigue
- Brain Fog
- Depression
- Increased heart rate
- Skipped heartbeats or heart palpitations
- Thyroid issues
- Brittle Nails
- Hair loss
- Pale Skin
- Poor sleep
- Anxiety
How Much Iron Do You Need?
Here are the recommended daily intakes of iron in healthy individuals according to the NIH :
Women
Ages 14-18 = 15 mg Iron/day
Ages 19-50 years = 18 mg Iron/day
Ages 51 and over = 8 mg Iron/day
Men
Ages 14-18= 11 mg Iron /day
Ages 19 and up = 8 mg Iron /day

What are the Best Foods for Boosting Your Iron?
Eating a diet of iron rich foods should always be your first priority when building up your iron. And getting lots of vitamin C can help increase iron absorption.
In food there are two types: heme iron and non-heme iron. Heme iron is iron that comes from the hemoglobin found in animal based food sources like meat, seafood, and chicken. Non-heme iron comes from plant-based sources like spinach and peas.
Heme-based iron can be found in foods like (per 3 ounce serving):
- Canned clams = 23.8 mg (12)
- Beef or chicken liver = 8 mg (13)
- Mussels = 5.7 mg (14)
- Oysters, cooked = 7 mg (15)
- Beef (3.5 oz.) = 2.7 mg (16)
According to myfooddata.com some of the best plant based sources of iron include:
Legumes (1 cup cooked)
- Lentils = 6.6 mg (17)
- White beans = 6.6 mg (18)
- Chickpeas 4.6 mg (19)
- Black-eyed peas = 5.2 mg (20)
- Black beans = 3.6 mg (21)
Leafy Greens & Veggies (1 cup)
- Spinach = 6.4mg (36% DV) (22)
- Swiss Chard (chopped) = 4 mg iron (22% DV) (23)
- Morel Mushrooms (chopped) = 8 mg (45% DV) (24)
- Asparagus = 4.13 mg (23% DV) (25)
Other Food Sources of Iron
- Dark Chocolate 70-85% cacao, (1oz square) = 3.7 mg iron (26)
- Pumpkin Seeds, unshelled (1 oz) = 2.29 mg (27)
- Oats (1 cup cooked) = 3.4 mg (28)
- Quinoa (1 cup cooked) = 2.8 mg (29)
See the full list of iron rich foods referenced here.
Even if you’re eating a balanced diet with a variety of different iron-rich food sources including meat, poultry, legumes, leafy greens, nuts, and seeds, taking a supplement might still be necessary to get your stores up to healthy levels.
 What To Do If You Have Low Iron?
What To Do If You Have Low Iron?
If you think you might have low iron, it’s important to have your levels tested by a doctor. Too much iron can be just as dangerous as too little. If it turns out you do need a boost, adding iron rich foods to your diet and a supplement to your daily routine will be your best bet.
What Is The Best Iron Supplement To Take?
There are a variety of different types of iron supplements to choose from. But they’re definitely not all made equally. Some are hard to absorb while others can cause really unpleasant side effects like constipation, abdominal cramping, and nausea. Others can make you feel energized in the short-term, but aren’t able to help you build up your iron stores in the long term to keep you healthy.
However, using a plant-based iron supplement can be a safe and effective way to increase and maintain your iron intake (30). Plus, no more of those nasty side effects.
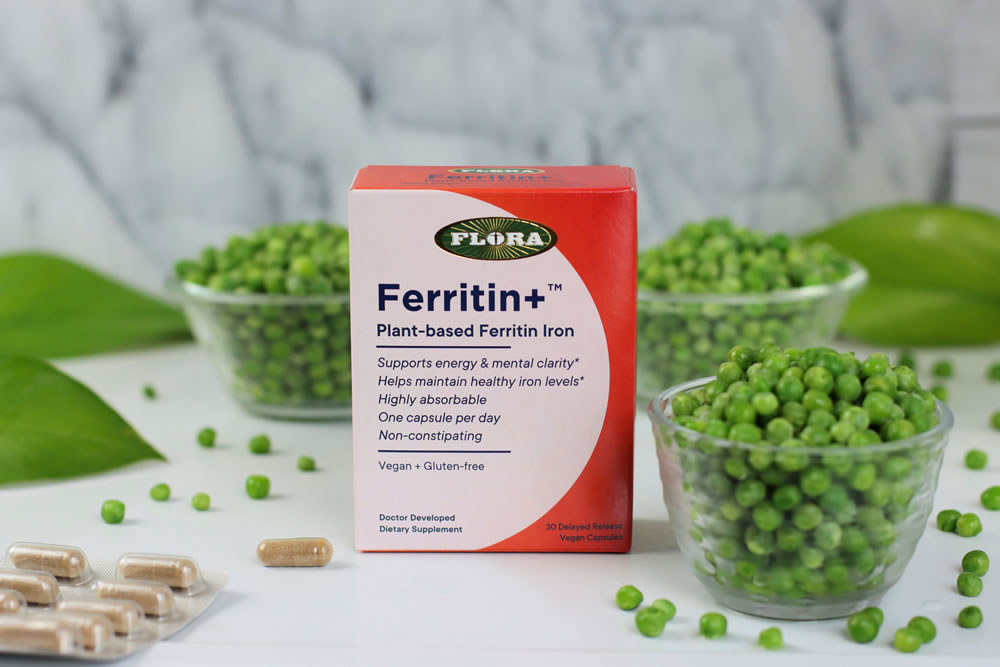
One breakthrough, plant-based, iron supplement called Ferritin+ from Flora Health is an iron supplement made with naturally iron-rich, organic peas. Iron is extracted from peas in the form of a protein called ferritin which is easily absorbed. For maximum effectiveness, Ferritin + capsules are naturally enteric-coated to protect the ferritin protein from being broken down by stomach acid. Ferritin+ is then slowly released and fully absorbed once it enters the gut. (31)
This helps to minimize digestive upset and maximize effectiveness. It’s a win win!
Taking Ferritin+ can help to:
- Support energy & mental clarity*
- Prevent iron deficiency anemia and boost energy*
- Support the production of healthy red blood cells*
With only one capsule needed per day, supplying 111% of your RDI of iron per day, Ferritin+ is a safe and gentle, slow release form of iron that is:
- Non-irritating and non-constipating
- Gluten-Free
- Vegan!
Great whether you’re vegan, vegetarian, or omnivorous, Ferritin+ is a gentle way to get your iron levels where they need to be so you can get that pep back in your step.
If you’re feeling low and slow, be sure to have your iron levels tested by a doctor to know where you stand before starting a supplement.
If you think you would benefit from a plant-based iron supplement, visit Flora Health to give Ferritin + a try!
Better Living uses affiliate links. If you make a purchase through them, we may receive a small commission (for which we are deeply grateful) at no cost to you.



